
Table of Contents
Explanations for correct installation
The first row of blocks is laid on a layer of mortar levelled on both sides.
horizontal and transverse.
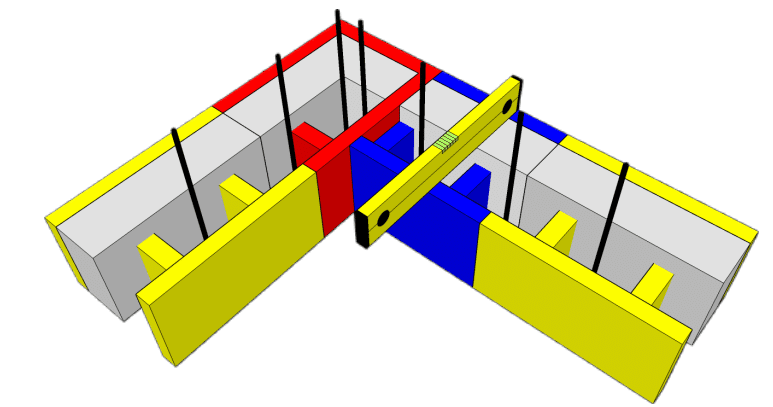
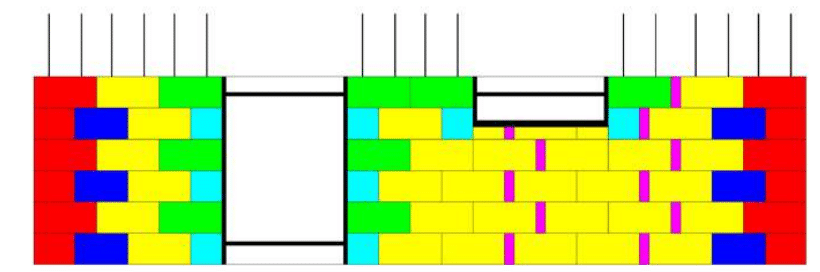
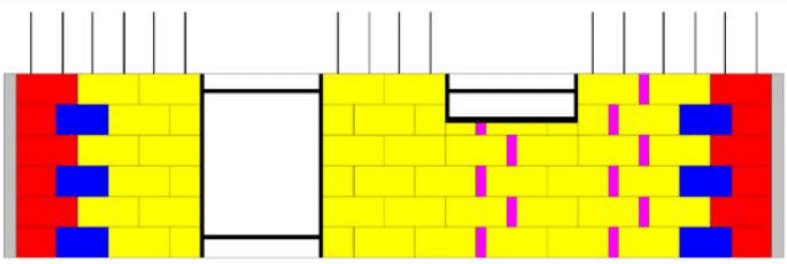
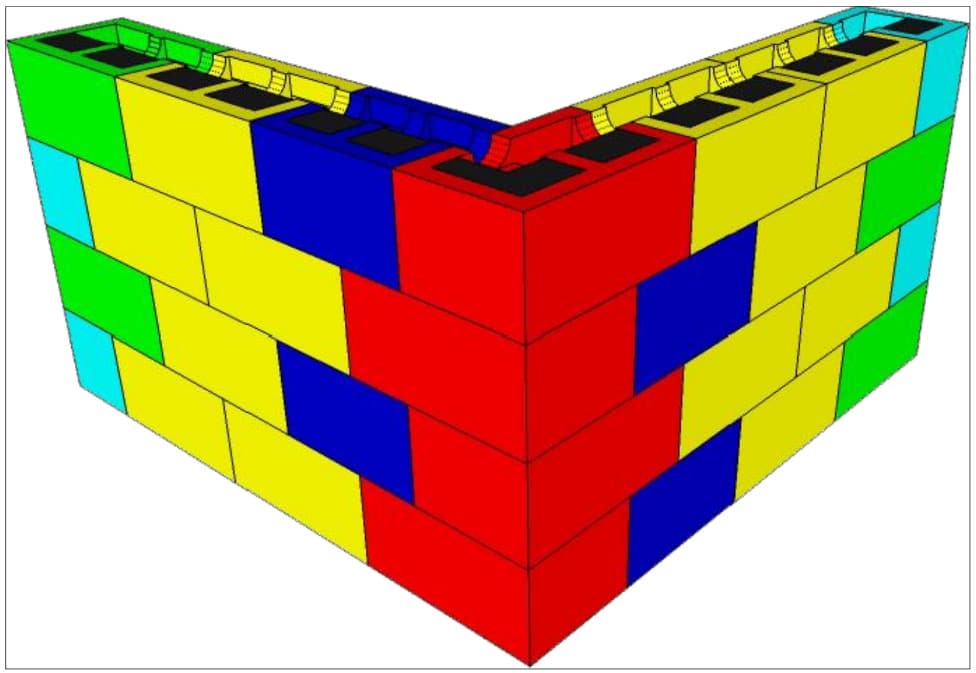
The following layers are laid dry, staggered by half a block (or block
pass), inserting a single or double horizontal reinforcement according to the project specifications.
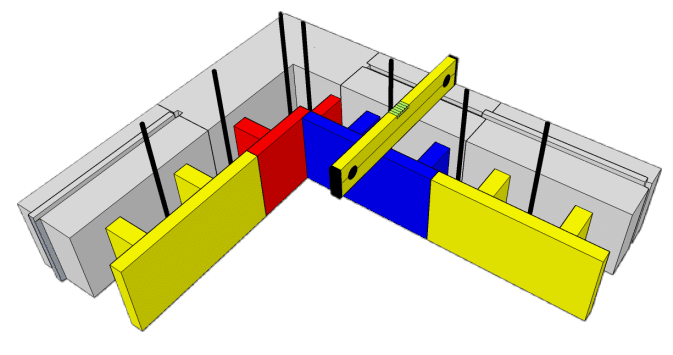
Once the height of 150 cm has been reached (6 rows), backfill with concrete to within 10 cm of the edge of the last row.
Immediately afterwards, the vertical irons are inserted by at least 60-70 cm for the following rows.
By repeating the same dry-laying operation, the desired height is reached using a series of special pieces cut to size, such as an extension or a fascia board.
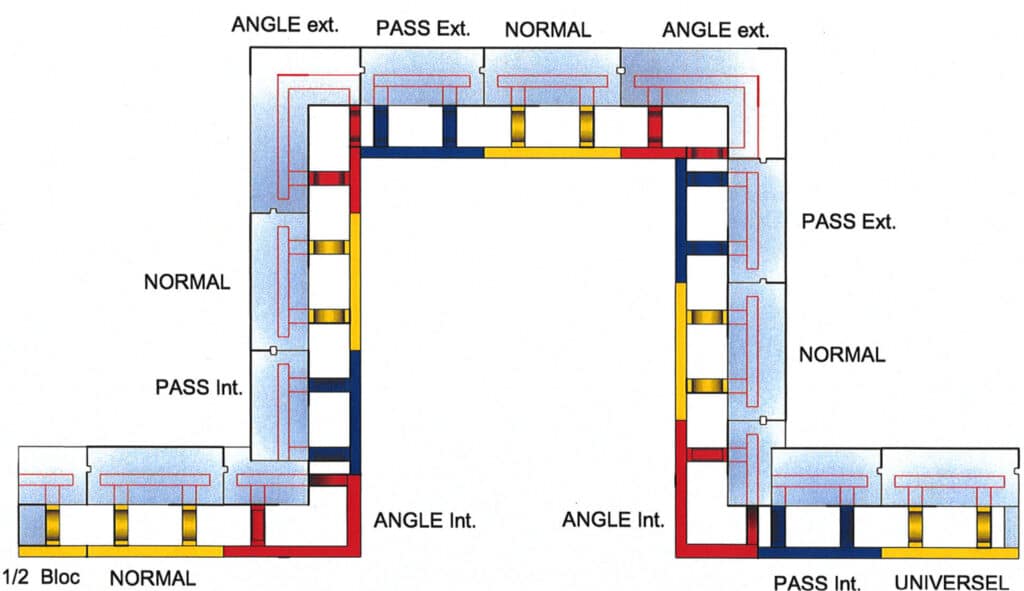
- Block H -
Assembling the wall with the various blocks
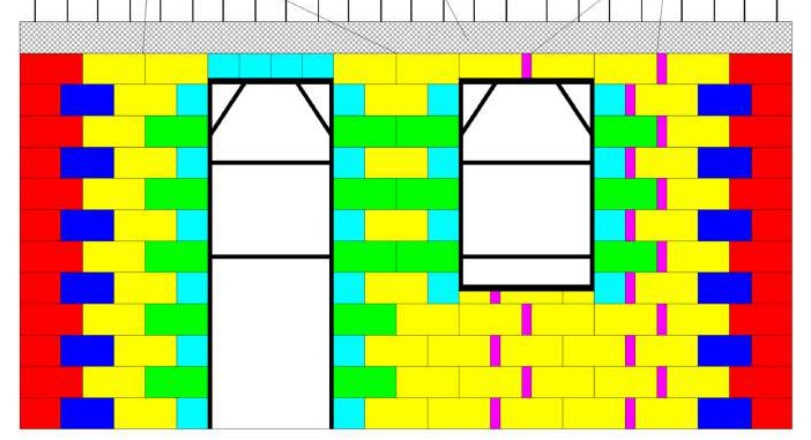


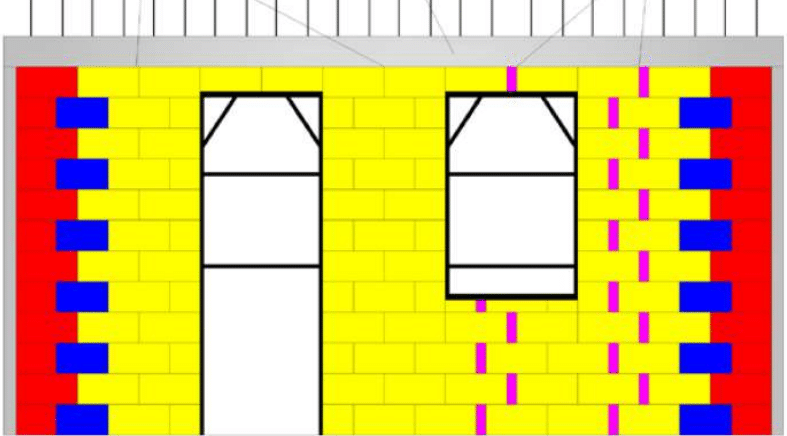
- HI blocks -
Assembling the wall with the various blocks

Applying plaster to interior walls
Any type of mixture based on gypsum, hydrated lime, perlite and specific additives can be used.
Allow to dry completely (15/20 days) before applying the finishing coat of fine mortar or plaster and lime coating.
BLOCS H: application for exterior walls
Any type of lime and cement-based mix can be applied once the walls are completely dry.
It is not advisable to apply the rendering at temperatures below 4°C. The thickness must not be less than 2 cm and should be applied in two passes, each 1 cm thick.
Leave to dry for at least 30 days at temperatures above 10°C.
Once fully cured, the following finishes can be obtained:
- Apply a water-repellent exterior mortar and stucco a fibre mesh and finish with a colour tint.
- Apply the coloured plaster using a smooth trowel and finish with a trowel.
BLOCS HI: application for exterior walls
- For the exterior finish, use a first coat of insulating plaster.
- Staple a fibreglass mesh, overlapping it by at least 10 cm.
- Then cover with a second coat of surface dressing.
- Once completely hardened, apply a primer and finish with a coloured coating applied with a smooth trowel.
Other advice
Block cutting
The cut must be as precise as possible to avoid thermal bridges and allow rapid assembly. The central part of the block should be removed to preserve the two ends of the block.
A number of tools can be used, such as a zag saw (accurate but lacking in efficiency), a sabre saw (fast, but precision will depend on the operator) or a band saw (preferred tool for the quality of the cuts and speed of execution).
Gluing will enable the block to withstand the load of the concrete and also to hold in place while the walls are being erected. The two parts of the block will be glued together, and the adjoining blocks will also have to be glued.
PU adhesive is recommended for its good hold and excellent mechanical resistance.
Treatment of window sills
All windows on the market are compatible with the Fixolite system.
Before fitting the window sill, insulation should be placed in the cavities of the block to avoid thermal bridges. The customer will supply, cut and glue these elements. To complete the insulation, the notches will also need to be filled. A thickness of 80 mm of Styrofoam insulation is recommended.
The window sills will be glued with PU adhesive. A bead will be applied to the wood fibre/cement assembly to ensure moisture and air permeability. A pump seal will complete the seal at the block/sill connection (inside).
Additional insulation will be added in front of the sill (on the inside) to complete the insulation. XPS is recommended for this additional insulation.
Floor treatment
All floors on the market are compatible with the Fixolite system. After cutting the blocks, the floor is positioned on the block wall.
The floor will be supported by props; under no circumstances should the blocks be used to support the floor before and during pouring.
It is also advisable to refer to the floor manufacturers' recommendations before installation (floor thickness, weight, etc.).
Flow station
A cutting station will have to be adapted to the constraints of the site, to enable tracing, perfect cuts and gluing.
Several saws can be used, such as a hand saw (accurate but not very efficient), a sabre saw (fast but not very accurate) or a band saw (fast and accurate).
Hot-wire cutting is recommended for cutting insulation, to achieve the precision required for fitting joinery.
Gluing
Pu glue (Kleiberit 501 Pu for example) is recommended for its various qualities, such as good resistance to heat, weather and particularly humidity. Clean, dry products should be glued in accordance with the adhesive manufacturers' recommendations.
Storage
The blocks should be laid on bastaings or pallets to avoid overhangs that could damage some of the blocks.
Blocks must be stored on level, clean ground to avoid soiling in the event of rain.
If it rains or if the blocks are stored for a long time, it is advisable to wrap them to prevent them becoming overweight during assembly (which can double in the presence of water) or in the presence of mud (not recommended for coatings). The presence of water will not facilitate cutting or gluing.
However, water has no impact on the quality of the wood/cement fibre. As the block is mineralised with lime, the wood is rot-proof.
Block assembly
At the openings : As the installation of joinery is recommended in tunnels, the joinery reservation plans (finished dimensions of the joinery) must be obtained (all manufacturers of openings provide this information). The blocks should be installed with the overall dimensions +10 mm to ensure watertightness. The same information should be requested for garage doors or other joinery.
Gluing blocks is recommended as soon as a block has been cut. This makes it possible to reconstitute the block into a single element after cutting, and it is also necessary to glue this block to the others to reinforce the whole.
Gable ends : For the top of the gables, gluing the blocks is also recommended. This ensures that the blocks are held in place when they are marked out and cut. In this case, the glue used could be wood glue.
Fitting swing shutters
Hinged shutters must be fixed to the concrete wall. The most common solution is to use chemically sealed threaded rods. However, it is advisable to follow the recommendations of the shutter manufacturer and use his materials.
The closure manufacturer should be informed of the thickness between the hinges and the concrete shell so that they can supply the appropriate materials.
Fitting the joinery
Fixolite blocks can be fitted with a wide range of fixings. Tunnel and rabbet fixing are the most common. There are several possible fixing systems: fixing from the concrete wall (recommended by the CSTB), fixing to the wood fibre/cement (density 510 kg/m3) or fixing into the insulation (by adding a stud).
Whatever the case, the recommendations of the opening manufacturers should be followed to ensure that the assembly is watertight and resistant.
Passage of technical ducts
There are two possible solutions:
- In most cases, ducts (water or electricity) are positioned within the thickness of the concrete shell. However, care must be taken to ensure that this does not affect the overall performance of the structure, and a concrete study should be carried out to validate this possibility.
- Fixolite blocks can also be grooved (after the concrete has been poured and dried) to allow technical ducts to pass through. Since Fixolite blocks do not add any mechanical strength to the structure, grooving can be considered. This method is mainly used on projects where the continuity of the concrete walls cannot be altered (acoustics, fire resistance, for example).
Balcony
Thermal breaks must be used to limit thermal bridges.
Coatings
Some coating manufacturers offer recommendations that have been tested on test sites. You should ask plaster manufacturers about the best solutions, which will take into account a number of factors, including geographical location (seaside, mountains, etc.) and the period during which the plaster is applied (frost, heat, rain or sunshine).
These recommendations also state that renderings must be reinforced on all facades. The type of reinforcement (PVC or steel) will be defined by the rendering manufacturers according to the type of rendering recommended.
Base elevation
Fixolite blocks should be used for basements (or basements) to avoid thermal bridges.
Recycling
- Insulation: this should be separated from the wood fibre/cement and taken to a recycling centre. As the insulation is not glued, separation is quick and easy.
- Wood fibre/cement : As wood is mineralised with lime (a natural treatment), these elements can be stored with the rubble.
